NEW CSH STUDY FINDS BIG BEHAVIORAL GENDER DIFFERENCES DURING CORONA LOCKDOWN
How do communication or movement patterns change in an acute crisis? Hub researchers see major trends in anonymized telecommunication data—and identify clear gender differences.
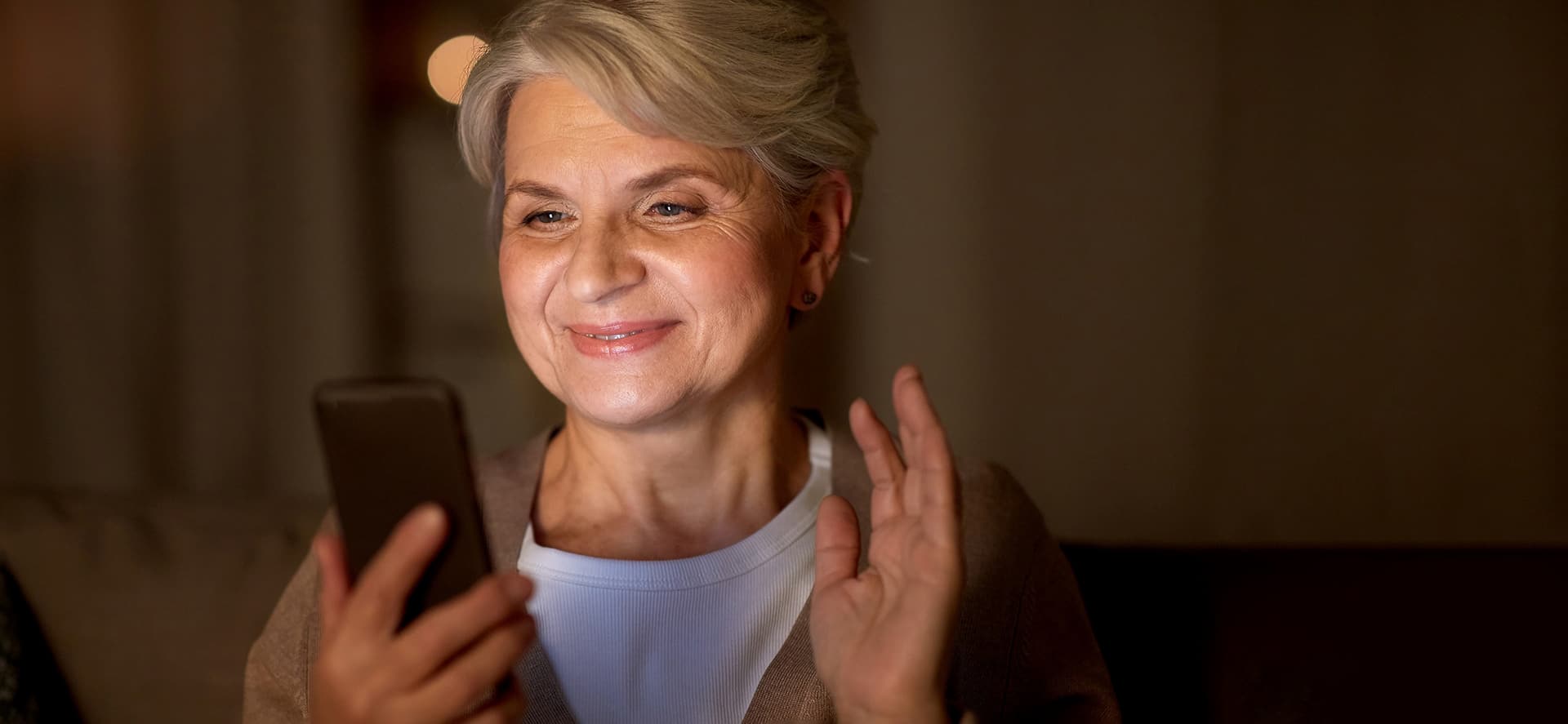
In a crisis, women make significantly longer phone calls and adhere more closely to governmental measures than men; men are less likely to have their mobility restricted and return to normal more quickly than women. CSH scientists found cliché-sounding behavioral patterns like these in data from the first Corona lockdown in spring 2020.
For their study—it just appeared in the journal Scientific Reports—Tobias Reisch and Georg Heiler as first authors evaluated mobile phone data from 1.2 million Austrians—about 15 percent of the population—between February and June 2020. The otheer authors are CSH scientists Jan Hurt, Peter Klimek, Allan Hanbury, and Stefan Thurner
MEN AND WOMEN BEHAVE VERY DIFFERENTLY
“The total shutdown of public life was like a population-wide live experiment,” Tobias points out. In spring 2020, the Hub was given access to anonymized telecommunication data from a major Austrian internet service provider. The scientists used the data to observe, with a slight time-lag, people’s mobility behavior.
“We were interested in the extent to which people supported the anti-Corona measures imposed by the government,” Tobias says. “When we analyzed the data by gender, we found surprisingly strong behavioral differences between men and women.” (Note: The gender categories are self-reported and are, for technical reasons, limited to female and male.)
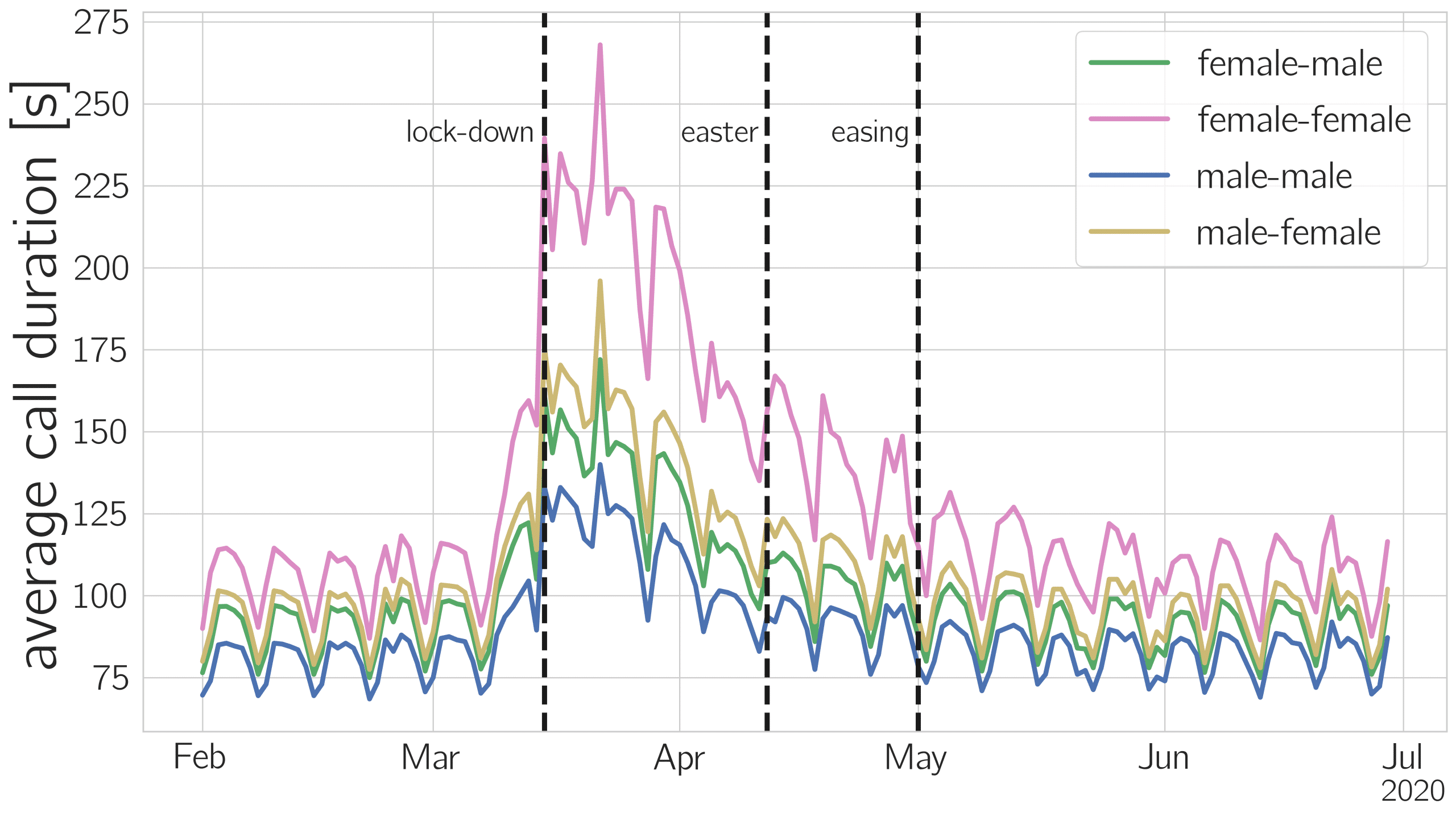
WOMEN MAKE LONGER PHONE-CALLS, MEN GO OUT MORE LIKELY
People made much longer phone calls right after the lockdown was imposed. “Interestingly, they talked to fewer people than usual—but with these few, they spoke longer,” Tobias explains.
As the figure shows, phone calls involving women lasted significantly longer on average, with big differences depending on who was calling whom. After the first lockdown in Austria was imposed on March 16, women to women calls were up to 1,5 times longer than before the crisis (+140 percent), calls from men to women lasted nearly twice as long. Conversely, when women called men, they talked 80 percent longer, while the duration of calls between men rose only by 66 percent.
“Of course, we don’t know the content or purpose of these calls,” adds Georg, who was responsible for data processing. “Yet, literature from the social sciences provides evidence—mostly from small surveys, polls, or interviews—that women tend to choose more active strategies to cope with stress, such as talking with others. Our study would confirm that.”
The scientists also found that already existing differences in the mobility behavior of men and women were massively amplified by the lockdown, with women limiting their mobility significantly more and for longer than men.
The more detailed evaluation of telecom data gained from a large recreational area in Vienna and from a shopping mall shows that both regions were more likely to be frequented by men during the lockdown. Also, after the measures were lifted, men returned more quickly to their pre-pandemic mobility patterns.
A VALUABLE SUPPORT FOR SOCIAL SCIENCES
“This study shows once again that data—in this case telecommunication data—allows us to gain social insights quickly and at low costs, without violating the anonymity of individuals,” adds our President Stefan. “We see people’s behavior in the here and now without the need for large surveys of thousands of people.”
On the one hand, this offers quantitative support for research questions in psychology and the social sciences—including interesting new questions emerging from data evaluations. “On the other hand, we are providing concrete information for policymakers which can either be used for planning in an acute crisis, or flow into a more targeted health planning, or could even lead to considerations on how to achieve a more gender-equitable society,” Stefan concludes.
The study “Behavioral gender differences are reinforced during the COVID-19 crisis” was published in the journal Scientific Reports on Sept 28, 2021.